If you’re describing nearly free and unlimited electricity as a problem, you may want to reconsider some things.
It’s a very capitalist way of thinking about the problem, but what “negative prices” actually means in this case is that the grid is over-energised. That’s a genuine engineering issue which would take considerable effort to deal with without exploding transformers or setting fire to power stations
Home owned windmills, solar panels and battery storage solves that.
Edit: Look at this awesome diagram of how it’s done for a hybrid setup that’s about $400 on Amazon.

Home owned windmills are almost a total waste. Its surprising how little electricity they generate especially given how much the cost to buy and install. Some real numbers. A 400w can cost almost $18k to buy and install. A 410w solar solar panel is about $250 + $3k of supporting electronics and parts. And that same $3k can support 10+ more panels. I looked into it myself really wanted it to be worth it for home, but it just isn’t. Now utility grade wind? Absolutely worth it. You need absolutely giant windmills with massive towers, but once you have those, you can make a LOT of electricity very cost effectively.
Solar panels worth it? Yes. Absolutely.
Batteries, not quite there yet for most folks. Batteries are really expensive, and don’t hold very much electricity $10k-$15k can get you a few hours of light or moderate home use capacity. For folks with really expensive electricity rates or very unreliable power this can be worth it financially, but for most every else. Cheaper chemistry batteries are finally starting to be produced (Sodium Ion), but we’re right at the beginning of these and there not really any consumer products for home made from these yet.
Yeah, right now end of life EV batteries are great for making your own power storage but that’s a level of diy beyond what 95% of people are willing or able to do
What’s infuriating is that we had electric cars before ICE powered cars. 1899. If we would’ve been investing money and effort into research for battery technology since then, we wouldn’t have this problem. Salt batteries, solid state batteries, and other promising tech is in it’s infancy because we just started to take this seriously as a society like 10 years ago.
Better late than never but it grinds my gears that the best argument against solar and wind is power storage requirements due to unpredictable power generation. Like this is an extremely solvable problem.
Yeah, right now end of life EV batteries are great for making your own power storage but that’s a level of diy beyond what 95% of people are willing or able to do
End of life EV batteries are great for grid-scale operators doing power storage, but I highly recommend against homeowners use them this way. Not just because they are complex DIY projects as you point out, but because the EV batteries that are aging out of car use are NMC chemistry. These are great for high density power storage, which you want in a car, but they are susceptible to thermal runaway if they get too hot. The original Tesla Powerwall and Powerwall 2 also used these same chemistry batteries. I wouldn’t want these in my house. However, in a utility grid scale? Sure, they won’t be anywhere near people so in the unlikely event they do catch fire its a property problem, not a lost human life problem.
I understand your concern, I totally agree that the volatility isn’t ideal, but putting it in a steel box outside your house isn’t that beyond the scope for a diy-er. Envision it the same way a generac sits outside and ties in to your house but with a safe enough enclosure.
As long as you check the cells you use when you deconstruct the car battery it should be fine. All the projects I watch online they don’t even need the liquid cooling system that it utilized when it was in the car because the discharge rate is so far below the C rating the battery that they don’t generate great like when they are in cars
I understand that cell could go bad though at any time, so the box is necessary imo
Sodium ion batteries are going to be the solution. 18650 packs are already out and perform economically. Since the molecules are so much bigger, energy density is only like 60% of lithium based solutions, but they have a very wide temperature range and are incredibly more inert and safe and density isn’t a problem for bulk energy storage.
The hurdle to overcome in inverters dealing with the very wide voltage span and bespoke charging ICs, but definitely possible and within 5 years will probably become a lithium iron phosphate competitor.
Oh yeah, super expensive. /s
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B087BY2YV7/?
The first link that came up: https://www.bobvila.com/articles/best-home-wind-turbines/
Ahh I get it now. You have no idea what you’re talking about. You have the smallest understanding of something and assume that is everything. You’re so very far away from understanding the practical applications and limits. You’re also clearly not interested in learning, so I’ll leave you to your impractical delusions.
Oh I’m willing to learn. Explain it to me.
Did you not look at the specs on that product? It only produces energy when winds are above 7mph and don’t actually hit the rated output unless the winds are almost 35mph.
Almost none of the country averages an amount of wind power per square meter equivalent to the rating on home turbines at 10 meters above ground level (yellow and red on this map):
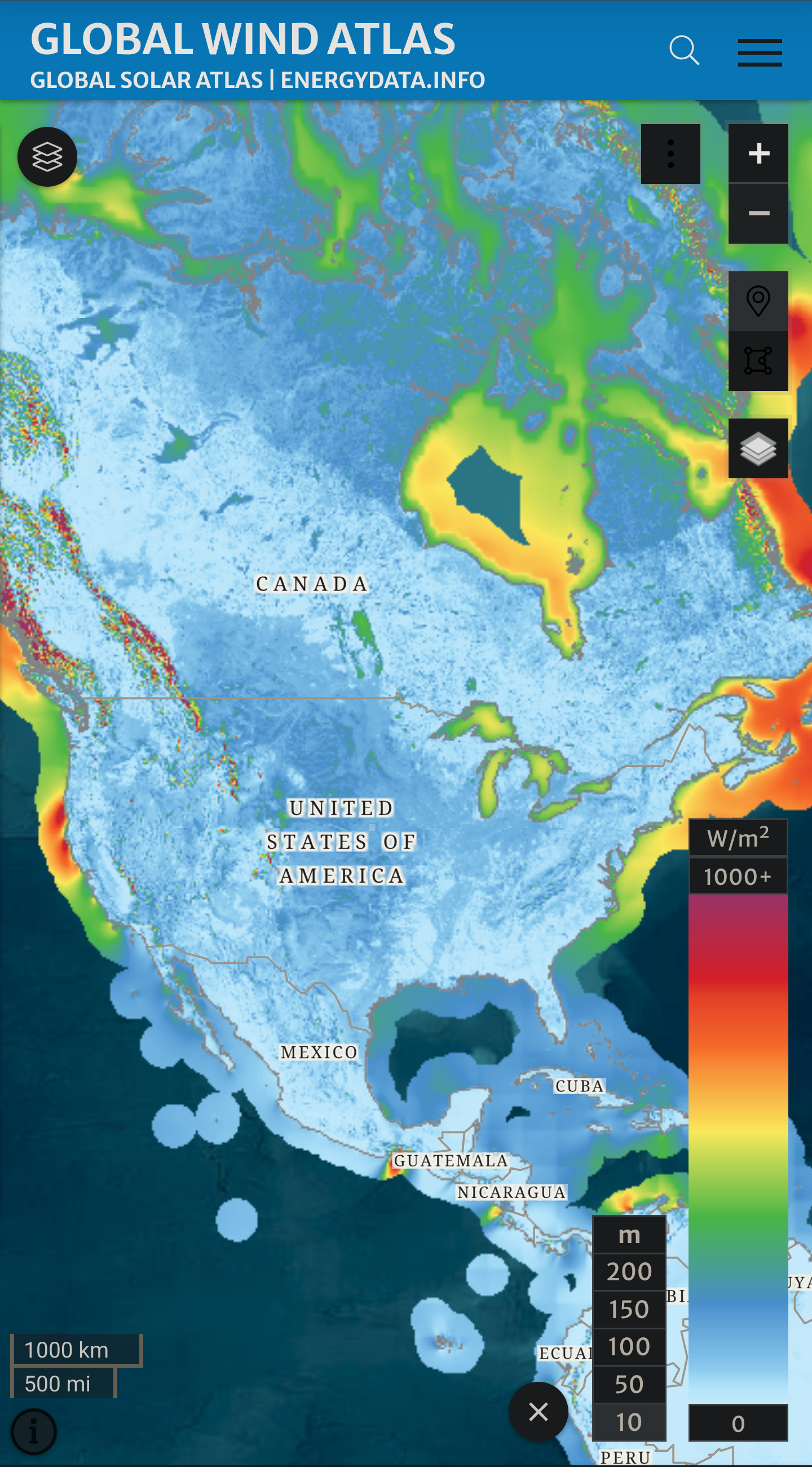
Compare to this map of average insolation:

It’s a hybrid solar and wind. Also, that’s why you have batteries for storage.
Why not skip the middleman and go straight solar, then?
Wait so the same people that can’t drop 500 USD for an emergency are expected to drop 300 USD for a wind turbine and provide the installation of it to boot is that right
“put the excess energy into batteries” is an idea, and is already pretty much what is done, but the large scale implementation still requires a lot of time, effort, and expense.
In no home outside of fringe uses are any lights 12vdc, with the exception of maybe led strip lights for undercabs. They’re all designed for 120vac. That lightbulb in the diagram is an e37/medium base for 120vac.
The grid is always over energized. That’s not a problem. Large solar and wind farms connect to the grid with great specificity about the maximum amount of energy they will put on the lines. The problem would be not enough energy. Batteries are beginning to solve the dispatch energy issue with renewables. As long as republicans don’t get their way and ruin renewable energy with unfair fossil fuel mandates, the grid will continue to modernize in this way and we’ll be fairly independent of fossil fuels in the future for electricity.
deleted by creator
deleted by creator
You can have your own batteries as well. If those then get overloaded, disconnect.
Nothing an open/close gate couldn’t fix. The real problem is how overly complicated we feel we need to make things.
This is some real “basic biology” level thinking here. Even if it were as simple as “Pull the lever Krunk!” then you’ve just turned all that solar infrastructure into junk for the majority of the time that we need power.
People use the vast majority of electricity in a day in the afternoon and at night - times that are noticeably after the peak solar production time. So you have all that energy going into the system with nowhere to go because battery technology and infrastructure isn’t there, and then no energy to fulfill the peak demand. This is an issue nuclear runs into as well because a nuclear plant is either on or off and isn’t capable of scaling its power to the current demand.
There are times where power companies have to pay industrial manufacturing facilities to run their most energy consuming machines just to bleed extra energy out of the grid to keep it from overloading and turning into a multi-million dollar disaster that could take years to get people back on the grid.
Sorry for the naive question, but is it not possible to send the excess electricity to the ground (in the electrical sense)?
To effectively waste electric power like that would take quite a bit of effort. It would be easier to make a giant heater that heats up air. But that would of course also be absurd. Just turn off the wind turbines etc. to reduce power generation.
It would definitely need to be ground in a literal sense.
And even the earth has its limits. Soil is only so conductive, pump enough energy into it and you’ll turn it to glass (which won’t conduct anymore).
Not an engineer but I sometimes watch them on YouTube.
Could you not just set up a breakout point and have it arc to ground? If the power source is renewable then wasting a little when you have a full grid shouldn’t be a big issue. I’m thinking something along the lines of StyroPyro’s arcing plasma flamethrower should chew up plenty of excess power if you scale it up. As you ramp your total storage up toward 100% capacity I’d start shutting off inputs (disconnecting solars, etc) and then have what’s basically a big old Tesla coil to vent excess power over 95% capacity.
Oh, look! A challenge. And a business opportunity! Just get a mortgage, buy some land in the middle of nowhere and make a reverse hydro plant.
Oh, I forgot. Banks don’t loan money for stuff not already existing or net-harmful hyped-up bullshit like AI and crypto.
In fairness, capitalist expansion is predicated on generating and reinvesting profit. If you build an array of solar panels and generate a revenue less than the installation+maintenance cost of the panels, you don’t have any more money to buy new panels and expand the grid.
That is, under a privatized system, anyway. If you’re a public utility and your goal is to meet a demand quota rather than raise revenue for the next round of expansion, profit isn’t your concern. You’re looking for the lowest possible installation/maintenance/replacement cost over the lifetime of the system, not the high margins per unit installed.
Incidentally, this is why vertically integrated private firms that consider electricity an expense rather than a profit center have been aggressively rolling out their own privately managed solar/wind arrays. When the concern is minimizing cost rather than maximizing revenue, and you can adjust your rate of consumption to match the peak productive capacity of your grid, then solar/wind is incredibly efficient.
thats why Westinghouse had to crush Nikolai Tesla. you can’t meter wireless power.
It’s how capitalists think about land, water, air, etc.
… And violently attacking people by depriving them of these needs.
I see this posted a lot as if this is an issue with capitalism. No, this is what happens when you have to deal with maintaining the power grid using capitalism as a tool.
Power generation needs to match consumption. Always constantly the power grid must be balanced. If you consume more than you can generate, you get a blackout. If you generate more than you use, something catches fire.
Renewables generate power on their own schedule. This is a problem that can be solved with storage. But storage is expensive and takes time to construct.
Negative prices are done to try and balance the load. Its not a problem, its an opportunity. If you want to do something that needs a lot of power, you can make money by consuming energy when more consumption is needed. And if you buy a utility scale battery, you can make money when both charging and discharging it if you schedule it right.
That’s not renewables being a problem, that’s just what happens when the engineering realities of the power grid come into contact with the economic system that is prevalent for now.
Also, fwiw, you can curtail wind turbines incredibly quickly. They’re the quickest moving assets on an electrical grid typically. So you are using them to balance the grid quite often. You can just pitch the blades a bit and they slow or stop. it’s not really a tech problem, but a financial one like you said.
I’m not sure much about solar curtailment, other than the fact that they receive curtailment requests and comply quite quickly as well.
Wind turbines like solar and BESSs are inverter-based resources (IBRs), so any of them can curtail quickly.
I’m not sure much about solar curtailment, other than the fact that they receive curtailment requests and comply quite quickly as well.
Here in the EU, the DC-AC transformers are mandated to shut down if the grid frequency is out of bounds.
I see this posted a lot as if this is an issue with capitalism. No, this is what happens when you have to deal with maintaining the power grid using capitalism as a tool.
The framing of it as the problem being that the price is going down rather than that excess power is feeding into the grid is what makes it an issue with capitalism. The thing you should be questioning is why MIT Technology Review is talking about some consequence of the problem that only exists because of capitalism instead of talking about the problem itself.
And before you downvote/object with some knee-jerk reaction that I’m being pedantic, consider this alternative way of framing it:
The opportunity is that solar panels create lots of electricity in the middle of sunny days, frequently more than what’s currently required, so it is necessary to develop new flexible sources of demand so that the excess energy doesn’t damage the power grid.
That’s pretty vastly different, isn’t it?
MIT Technology Review is talking
they did talk about this many years ago. This is a very old screenshot that has been around the internet for probably a decade at a guess. You might notice the check mark because this was from a time that twitter actually vetted sources. There’s nothing wrong with a publication having bad takes on occasion. That does happen now and again.
The telling part is the fact that this one single tweet keeps being reposted repeatedly, with the reply as if this is a substantive criticism of capitalism.
I don’t like using the term capitalism because it is too vague. Political corruption protecting oligarchy/big corporations is the problem.
Inflation resulting from start of full war on Russia and resulting oil/diesel price spike forced the wrong policy of higher interest rates. The theory in the past is that increasing austerity on consumers reduce their driving, and preventing business investment also reduces expanded demand for scarce FFs.
In the dynamics of energy disruption, high interest rates are the biggest cost obstacle for renewables and less new renewables is more oil/FF extortion power. At 2000 sun hours/year, $1/watt solar installation, could get a 16 year payback = 100% overall profit at 3c/kwh price. 2c/kwh at 3000 sun hours/year. Every 2% in interest costs, increases required price by 1c/kwh.
Protection of existing assets/supply scarcity is not affected by higher interest rates. New oil wells do have a big upfront cost, but they also have a huge power and maintenance requirement that is paid for with the product taken out of the ground, with ROI protections if renewables can be suppressed, including with high interest rates.
Political corruption favouring scarcity over abundance is the problem. Cheap energy or steel is a huge competitive and life quality advantage. Use cheap inputs for more productivity and happier life with cheaper cost.
That’s pretty vastly different, isn’t it?
Not really. It’s like saying toast falls butter side down, vs toast falls non-buttered side up?
Perhaps some are conditioned for an emotional response, rather than a rational one, upon hearing certain words? That’s why you suggest to avoid them, even to describe the same issue?
People are emotionally driven animals at the end of the day. As much as we try to argue otherwise, it’s our default state. It’s not conditioning, it’s nature. If you believe yourself to be otherwise, then you’re susceptible to being emotionally exploited without even realizing it. I had a coworker rant in circles for 2 hours the other week about how he’s very rational and how people need to stop reacting emotionally to things, while also going on about how Democrats are snowflakes and Republicans use facts and logic in their arguments, and how despite having trans friends, he’ll never see them as their actual gender because “basic biology” and people shouldn’t expect others to accommodate things like calling them by the right name.
That said, how you frame a problem can vastly affect how people consider solving it. A great example is one that somebody else posted in this thread talking about how sime companies that see electricity as an expense rather than something that reduces profits are actually moving towards building their own renewable energy infrastructure because it’ll drive their expenses down in the long run.
As much as we try to argue otherwise, it’s our default state. It’s not conditioning, it’s nature.
I think you’re excluding a large group of people (1). The nature vs nurture debate on that one isn’t clearly solved, but it seems one both needs the genetics and conditioning to arrive at an emotion based, rather than cognitive based, thinking system. Let alone to develop those specific triggers.
see electricity as an expense rather than something that reduces profits
An expense is something that reduces profit. They’re the same :)
Nice comment! Thanks.
Just to be clear this can’t be solved with storage. Currently it can be but not permanently.
For ease of argument let’s say the grid runs 100% on solar with batteries that last a day. For 100% solar you need to build power for when demand is highest, winter, and supply is lowest also winter. Come summer demand is lowest and supply is highest. You can’t store all that energy in summer because you got fuck all to do with it.
It’s a really weird cost saving exercise but basically when supply is massively abundant it has to be wasted. No one is going to build that final battery that is only used for 1 day every 10 years.
Bringing it all together. In a 100% renewables grid with solar, wind, hydro and batteries a lot of electricity will be wasted and it will be the cheapest way to do it. Cheaper than now.
Quite a few people talk about this on youtube. Tony Seba and rethinkx is the best place to start in my opinion.
Hydo power can be used as storage, and can generate power on-demand. I’d recommend avoiding YouTube if you want reliable information.
Yes it can, I didn’t say otherwise. I’m not sure what your point is.
The electricity grid is about matching supply and demand. Hydro is not going to stop massively amount of wind and solar being wasted in a 100% is it?
Also most grids don’t have enough hydro storage or inertia to solve to problem by itself.
You can’t store all that energy in summer because you got fuck all to do with it.
Main value of H2 electrolysis is solving (more economic return from renewables than just curtailing) this problem. Also provides exportable energy to cover winter clean power/heat needs.
I’ll be interested to see what happens with this.
New forms of industry will work out if you got very low capital costs and high energy costs. The factory is going to be running, what? At most 25% of the year? Probably more like under 10 and unpredictable. That’s going to be so weird for profitability.
I feel like storing the hydrogen itself could be an issue. Storing methane seems way easier so I wonder if that happens instead. But is it cheap to make a device that can make huge amount of hydrogen or methane? I have no idea and no one seems to know what’s going to happen yet.
I just expect most of it to be dumped. Because it’s 1 less thing to buy.
To get $2/kg 300 bar H2, $500/kw electrolyzer capital costs, and 2c/kwh electricity input costs are needed. China is pushing down to $300/kw on electrolyzer costs. Just as seasonal negative prices happen in some locations, stabilizing to 2c/kwh is the path H2 enables. $2/kg H2 means 6c/kwh CHP power cost from Fuel Cell, and 10c/kwh electric only power output. Competitive with electric utility service, and fast charging vehicle stations. It’s competitive at $4/kg in many jurisdictions, in fact.
Factories already operate mostly daytime. Solar output is seasonal with more variability the further from equator you go. Having solar cover 100% of summer cloudy day generation at low AC use, can result in 2c/kwh or less prices on sunny days, and in Spring and fall where there is no HVAC demand. Running FF electricity just in winter/backup is path to significantly lower emissions, and lower cost of FF energy from less use. Factories with long shifts running half on solar is still low overall energy input costs, if they can sell what they make.
H2 storage is a solved problem. Lined pipe and pressure vessels. If factories are ever automated to the point where labour cost is nearly irrelevant compared to energy costs, then they too can become variable loads. H2 electrolysis and desalination and battery charging are all highly automated processes that benefit from those conditions today.
The forever advantage of green H2 production is that it is containerizable. Can be transported seasonally to where renewable surpluses will occur. I guess self mobile robots could do the same, though.
I can’t ragebait if you people are being logical 😒
Something catches fire lol what, as if they can’t just disconnect the solar cells if they run out of batteries
You can do. If you don’t that’s when you get the fire, or more likely a whole bunch of breakers flip and you are in a black start situation.
This is a problem that can be solved with storage. But storage is expensive and takes time to construct.
true. thing is, they’ve seen it coming for a decade, and knew it needed to happen. It shames me that we’re just now trying to pick up the storage side when we’ve had ample evidence the need was growing rapidly.
batteries were (are) expensive and have been decreasing in cost partially because of electric vehicles investing in batteries earlier than necessary would give money to research that would otherwise be funded by others (a bad idea in capitalism unless you need the research quickly) and loans were cheap.
there are loads of way to store energy that don’t involve batteries. pumped hydro is excellent, for example. but there’s also flywheels, thermal salt, and a dozen other ways.
trust me, if we’d had a visionary in the white house instead of trump, we could have figured out some possible solutions to pursue.
instead we’re gonna waste more than a decade playing fuckaround while china builds thorium reactors, fusion, high speed rail to mongolia etc
Then tell me why the mechanism to control production via the solar panels themselves hasn’t been implemented? I’ve seen several viable options, including covers that are manual or even automated and powered by the excess energy…
South Australia has run into this problem and implemented a solution.
When the solar exports in a section of the grid exceeds the local transformer’s limits, a signal is sent to all of the inverters in that section to limit the export rate. The same signal can be send to all solar inverters in South Australia if the entire grid has too much renewable energy.
This signal only limits the export to the grid, so the homeowner can always use their own solar power first. The permitted export is guaranteed to be between 1.5kW and 10kW per phase.
The was a minor oversight during implementation. Homeowners on wholesale pricing would often curtail or switch off their solar inverters if the prices went negative. If the grid operator sent a signal to reduce the export rate, it would override the homeowner’s command and force a 1.5kW export during negative pricing (costing the homeowner to export). No-one considered that anyone might not want to export solar all of the time.
Then tell me why the mechanism to control production via the solar panels themselves hasn’t been implemented?
Why would you want people to tell you things that are untrue?
Capitalism does solve it. Eventually. It takes the information in steps and gets to a solution that experts were talking about decades before. This is not a good way to do things.
It tends to overinvest in the thing that has the most immediate ROI. That’s been solar. Wind/water/storage/long distance distribution are all important pieces of this, too, and this has been known in climate and civil engineering fields for a while. Solar can’t do it all by itself.
A sensible system would even out the investment in each. The wind often blows when the sun isn’t shining, so you don’t need as much storage to do the in between parts. Water not only provides an easily adjustable baseload (nuclear does not adjust very well), but it also doubles as storage. In fact, if we could link up all the hydro dams we already have to long distance transmission, we wouldn’t need any other storage. Though that isn’t necessarily the most efficient method, either.
What capitalism does is invest in solar, find that causes negative prices, and then invest in the next best ROI to solve that. Perhaps it’s storage. That results in a lot more storage than would otherwise be needed than if wind/water/long distance distribution were done alongside it. Or maybe the next best ROI is wind, but there are still lulls lacking in both sun and wind–as well as periods where you have too much of both–so you still need storage.
And what capitalism really doesn’t want to do long distance transmission. It’s not just big, but it’s horizontal construction. That means rights to the whole route have to be purchased. It means environmental concerns along the entire route have to be thought out. It means soil has to be tested for stability and footings made to suit for the entire route. Capitalism almost has to be beaten into submission for anyone to build anything horizontally. (See also: trains and highway systems, both of which came with substantial government investment and incentives).
Ughh, no, negative prices aren’t some weird “capitalism” thing. When the grid gets over loaded with too much power it can hurt it. So negative prices means that there is too much power in the system that needs to go somewhere.
There are things you can do like batteries and pump water up a hill then let it be hydroelectric power at night.
But it doesn’t say “it can generate too much energy and damage infrastructure”, they said “it can drive the price down”. The words they chose aren’t, like, an accident waiting for someone to explain post-hoc. Like, absolutely we need storage for exactly the reason you say, but they are directly saying the issue is driving the price down, which is only an issue if your not able to imagine a way to create this infrastructure without profit motive.
Yeah mate. The people writing here are economists not engineers, and that’s the professional language for what they’re talking about in their field. It’s like if a nuclear engineer said “oh yeah, the reactor is critical” which means stable.
I hear the point your making and the point OP made, but this is how really well trained PhDs often communicate - using language in their field. It’s sort of considered rude to attempt to use language from another specialty.
All of that context is lost in part b.c. this is a screenshot of a tweet in reply to another tweet, posted on Lemmy.
The way it’s supposed to work is the economist should say “we don’t know what this does to infrastructure you should talk to my good buddy Mrs. Rosie Revere Engineer about what happens.”
All I know about nuclear reactors is that prompt critical is the “Get out of there stalker” one.
Your prompts are especially critical when you decide to let ChatGPT run your reactor controls.
Economists think in terms of supply and demand. Saying it drives prices down or negative is a perfectly good explanation of a flaw in the system, especially if you’re someone on the operating side.
Boy do I hate economists.
Why? Economists ≠ capitalists.
Why is it a flaw from an economic perspective?
Both generation and consumption of electricity have a supply and demand. This is perfectly accepted in many other markets as well. We also had negative oil prices during the first Covid spike because the excavation cannot be stopped immediately. Certain industries like foundries also struggle with fully shutting down and restarting operations so sometimes they rather sell at a loss than stop operations. Farmers sell at a loss when the market is saturated just to sell somewhere and in other years they make a good profit on the same produce (assuming they actually have market power and aren’t wrung dry by intermediate traders).
In terms of energy per capital investment and running costs solar power is among the cheapest energy sources, cheaper than fossils and much cheaper than nuclear power. So it is profitable overall to run solar power, even if sometimes the price is negative.
Nobody here is suggesting that we should avoid solar power because of this.
But the point is that it is not even a flaw from an economic perspective. There is demand both for short term flexible and long term stable energy production and energy consumption in the grid. If you assume prices to be a suitable instrument, which most economists do, then the negative price of the production is a positive price for the short term consumption.
this feels like someone just looking for an argument… having negative pricing is a problem, and yes there are solutions like hydro and battery… hopefully this encourages that infrastructure to be created!
Except the grid overload thing isn’t even an issue with renewables, since wind can be shut down in a matter of 1-5 minutes (move them out of the wind) and solar literally just be disabled. Any overload they produce would be due to mechanical failure, where you can cut them off the grid since they’re in the process of destroying themselves anyway (like in those videos where wind turbines fail spectacularly). Otherwise renewables are perfect to regulate the grid if available.
In a hypothetical grid with an absolute majority of many badly adjustable power sources (like nuclear) you’d have to work with negative prices to entice building large on-demand consumers or battery solutions. So far nobody was stupid enough to build a grid like this though.
tl;dr, this whole problem indeed is about economics and therefore may very well be a “capitalism thing”. Renewables do not overload the grid.
That’s also a pretty naive take on it.
First of all, you can indeed shut of the renewables easily. But that means that adding renewables to the grid is even less profitable, making renewables less desired to be built.
Hence in for example Germany a law was passed that prevented renewables being shut down in favor of worse energy sources, but that then leads to the issue we mention here.
It’s a tricky situation with renewables. But on the other hand, society is slowly adapting to using them & improving the infrastructure to handle such issues, so we’ll get there eventually :).
Its not tricky, energy shouldn’t be privatized.
and that’s how you get laws preventing me from giving power to my neighbors when their breaker panel is getting replaced or the grid is down.
Not really, its how you stop paying entirely arbitrary prices for a monopoly.
Also what you’re suggesting is illegal in some areas, and that’s without true public utilities.
I agree that the grid should be a public utility, it’s just that the energy production makes some sense to be privatized (and have some pressure to use the public grid) because distributed supply (rooftop solar) allows for lower losses and with regulation changes could allow for less overprovisioned residential lines (have lower amperage service rates to incentivize people with solar to flatten their net power usage) and for car parking lots to have solar shading.
sounds like a great argument for nationalization.
I don’t understand why it’s profitability is my concern. Or anyones.
Because that’s what makes companies invest in renewables. If it’s not profitable, no new investments, and our world goes to shit (even more).
Caring only about profit is the exact reason why it’s going to shit. That is in no way the answer.
It may not be the answer, but it is the current reality. If we want more renewable power right now, it needs to be profitable.
You can wish it’s different, we all do. But reality is what it is, so that’s why you should care :).
Except no, all we need to do is just not allow these companies to impose laws and regulations that stop us from innovating. That’s exactly what’s Happening Here. They’re not improving to be a better service, they’re not making cheaper better energy. They’re using coercive legal systems to stop cheaper better energy from being created. Your entire premise is utterly flawed.
I feel like having a colossal battery pack could help with that problem.
Absolutely. The hydro thing is really just a water battery, it’s just stored in potential kinetic energy instead of chemical energy. But sodium cells are starting to look like a good option for chemical energy too.
It can, but people need to build it.
Colossal is an understatement
Yep, and the cost difference between those times should make this very cost effective.
negative prices aren’t some weird “capitalism” thing.
lmao.
🙄 It’s not like the need to get extra power out of the system magically goes away if money doesn’t exist.
Capitalism makes abundance problematic.
Supply side Jesus says put your faith in the wisdom of the CEO.
The answer is batteries. And dismantling capitalism, but batteries first
Nah, lets squash capitalism first.
Not saying we shouldn’t do both, but in reality waiting to destroy capitalism before fixing the grid just means you have too much theory and not enough praxis.
deleted by creator
Batteries for something like this would be something like a lake on top of, and at the bottom of, a mountain.
Then you use excess power to move water up, and when you need power, the water comes down through a turbine.
Honestly, this attitude is downright suicidal for our species right now. Capitalism took centuries to develop. Anything that replaces it will form over a similar time scale. And with climate change, that is time we do not have.
I’ve got some bad news though. If our markets keep ignoring the environmental cost of… well, pretty much anything, as they always have, capitalism will also fuck us over in the long run. I’ve even heard it’s already happening…
CapitalistsPeople in just about every system ignore negative externalities, which are defined as costs borne by other people for the benefits that they receive themselves. Ironically, capitalism might be the best short-term solution, if only we had the political will. One of the major functions of government is to internalize negative externalities, via taxes and regulations. It’s easy for a factory owner to let toxic effluent flow into the nearby river, but if it costs enough in taxes and fines, it’s cheaper to contain it. We just need to use government regulations to make environmental damage cost too much money, and the market would take care of re-balancing economic activity to sustainable alternatives. The carbon tax is a well-known example of this technique, but we’ve seen how well that has gone over politically. Still, it’s probably easier to push those kinds of regulations in a short time frame than to fundamentally revamp the entire system.A non-functioning government is also a feature of capitalism, though.
A big flaw in German energy policy that has done a great job in expanding renewables, includes not giving its industry variable rates, that lets them invest in batteries, and schedule production more seasonally, or if they have reduced demand due to high product prices from high energy costs, just have work on the good days.
Using EVs as grid balancers can be an extra profit center for EV owners with or without home solar. Ultra cheap retail daytime rates is the best path to demand shifting. Home solar best path to removing transmission bottlenecks for other customers. Containerized batteries and hydrogen electrolysis as a service is a tariff exempt path at moving storage/surplus management throughout the world for seasonal variations, but significantly expanding renewables capacity without risking negative pricing, and making evening/night energy cheaper to boot.
You can read the Technology Review article here discussing why this is problematic beyond a JPEG-artifacted screenshot of a snappy quip from a furry porn Twitter account that may or may not have read the article beyond the caption. We need solar power plants to reach net zero emissions, but even despite their decreasing costs and subsidies offered for them, developers are increasingly declining to build them because solar is so oversaturated at peak hours that it becomes worthless or less than worthless. The amount of energy pumped into the grid and the amount being used need to match to keep the grid at a stable ~60 Hz (or equivalent where you live, e.g. 50 Hz for the PAL region), so at some point you need to literally pay people money to take the electricity you’re producing to keep the grid stable or to somehow dump the energy before it makes its way onto the grid.
One of the major ways this problem is being offset is via storage so that the electricity can be distributed at a profit during off-peak production hours. Even if the government were to nationalize energy production and build their own solar farms (god, please), they would still run up against this same problem where it becomes unviable to keep building farms without the storage to accommodate them. At that point it becomes a problem not of profit but of “how much fossil fuel generation can we reduce per unit of currency spent?” and “are these farms redundant to each other?”.
This is framed through a capitalist lens, but in reality, it’s a pressing issue for solar production even if capitalism is removed from the picture entirely. At some point, solar production has to be in large part decoupled from solar distribution, or solar distribution becomes far too saturated in the middle of the day making putting resources toward its production nearly unviable.
In other words… Maybe 29 word Twitter captions aren’t a great way to discuss issues?
Nah, I see nothing wrong with an information diet composed of random people with no background sharing their pet conspiracy with 5 million people on TikTok that they learned from three minutes with ChatGPT, furry porn accounts clapping back on Twitter to an out-of-context 29-word quote from an MIT Technology Review article (reshared so many dozens of times that the quality has noticeably degraded), or a picture generated in a Russian disinformation farm showing a muscular Donald Trump rescuing crying orphans from drowning in Hurricane Helene while corrupt FEMA agents loot their houses.
God fucking help us.
But on the plus side,
On the plus side I guess: accessing good, robust information has literally never been easier as long as you’re media-literate enough not to fall into the landfill of trash information that you’re walking over.
- During its start in the 2000s and early 2010s, Wikipedia was like a shadow of what it is today. As an example, take a look at the article for the element oxygen in 2006 (ignore the broken templates) and the article today. Its editors were just as smart, well-meaning, and hard-working, but guidelines and a deeply entrenched culture hadn’t emerged around making sure things are as verifiable, reliable, independent, unbiased, inclusive, and comprehensive and as possible. It’s kind of insane how much you can find there now as a starting point for further research. Wikipedia also forced the web-ification of Britannica, meaning even if you deeply distrust Wikipedia for some reason, you no longer need to pay hundreds to have an encyclopedia in your home.
- Additionally, I imagine there are serious, experienced editors who are using LLMs to great effect as essentially a search engine on steroids to find obscure information, thereby speeding up their work (and they have the media literacy from years or decades of editing Wikipedia to wield this responsibly). Those who use it irresponsibly seem to be very quickly found out, although because I can’t prove a negative, I can’t say how much slop has slipped through the cracks.
- Extremely niche hobbies and specialties have e.g. YouTube channels, subreddits/communities, etc. dedicated just to them providing a fantastic wealth of knowledge. Right now, I can go watch Gutsick Gibbon on YouTube to catch up on various findings in primatology from a PhD candidate on the verge of becoming a doctor. I can watch Gamers Nexus for highly comprehensive breakdowns of tech products. Realistically, I can self-teach in ways I never could have 20 years ago as long as I’m responsible.
- Piracy has arguably never been easier to gain access to paywalled research papers, books, etc. There’s a movement in academia to make research open-access.
- Software is moving more and more toward open-source. This gives entrenched, capitalist power structures increasingly limited control over people and opens up this knowledge to everybody.
That all being said, things are really dire because so many people really lack the basic media literacy skills to utilize these tools and avoid the ocean of shit around them.
It’s a bit scary because many of those things (Wikipedia, academic piracy) are being threatened and villainized, others (Reddit niches, maybe eventually YouTube) are hemorrhaging useful info, and utilitarian LLMs are simultaneously being vilified and enshittified by opposing political sides.
Like, with the Qwen3 release, I just realized my internet barometer for “is it any good?” and technical info is totally gone… Reddit and other niches have withered away, Twitter/Linkdin are pure engagement farms, and I can’t hardly discuss it anywhere else populated without getting banned as an alleged AI Bro (whom, for the record, I hate with a burning passion). I seriously considered joining WeChat just to see some sane discussion.
This is true for other fandoms and niches I’m in.
I hate to sound apocalyptic, but it feels like my information sphere is imploding. The real marker will be when the US government starts taking action against Wikipedia.
America: …Nah, this is fine. In fact, let’s elect the platforms’ owner-influencers. scrolls happily
In other words… Maybe paragraphs of word salad aren’t a great way to debunk an obvious truth?
I found the post to be succinct and coherent.
Some problems need 2 or 3 paragraphs to even begin to convey them. They could’ve said “the problem isn’t just capitalism,” and that would have been met with vitriol, as it doesn’t convey that the actual article is more nuanced than “anti solar,”that meeting variable power demand with solar supply is a challenge, that at some point one does indeed saturate regional demand for solar to the point that building more plants isn’t productive (which frequent negative prices are an indication of), and so on.
And if that’s too long and complex, well… I dunno what to tell you.
I do like how this Twitter account, in the rush to blame capitalism, overlooked the fact that the sun rises and sets every day.
I’ve known about the issue with a lack of ways to store the energy produced for about 5 years now, does it seem like we’re making any steps in it recently? Also how does it work in a “green” fashion to produce all of the batteries necessary for that sorts of energy storage, I feel like that’s going to be one of the next discussions about how “pure” this method is.
The size of the storage problem is not well understood by most. The world production of batteries is insufficient to power germany with 100% renewables.
A possible solution is changing consumption patterns (in jargon known as demand-response). This runs into 2 issues: (1) people need to change their behaviour, with they wont. (2) You handicap your economy, to the benefits of countries that do not care about emissions. With a good chance that the net result is more emissions.
It’s funny how capitalist apologists in this thread attack the format of a tweet and people not reading the actual article, when they clearly haven’t read the original article.
Negative prices are only mentioned in passing, as a very rare phenomenon, while most of it is dedicated to value deflation of energy (mentioned 4 times), aka private sector investors not earning enough profits to justify expanding the grid. Basically a cautionary tale of leaving such a critical component of society up to a privatized market.
Without reading the article, I could already see what the problem was.
Unless you have capital to invest, you can’t expand or improve the power grid. That capital can either come from the gov’t–through taxation–or from private industry. If you, personally, have enough capital to do so, you can build a fully off-grid system, so that you aren’t dependent on anyone else. But then if shit happens, you also can’t get help from anyone else. (Also, most houses in urban areas do not have enough square feet of exposure to the sun to generate all of their own power.)
Fundamentally, this is a problem that can only be solved by regulation, and regulation is being gutted across the board in the US.
That’s not the problem the article gets to. The capital is there. Capital is being dumped into solar at breakneck speed. That’s the problem.
As more solar gets built, you get more days when there’s so much excess solar capacity that prices go near zero, or occasionally even negative. With more and more capacity around solar, there is less incentive to build more because you’re increasing the cases of near-zero days.
Basically, the problem is that capitalism has focused on a singular solution–the one that’s cheapest to deploy with the best returns–without considering how things work together in a larger system.
There are solutions to this. Long distance transmission helps areas where it isn’t sunny take advantage of places where it is. Wind sometimes blows when the sun isn’t shining, and the two technologies should be used in tandem more than they are. Storing it somewhere also helps; in fact, when you do wind and solar together, they cover each other enough that you don’t have to have as much storage as you’d think. All this needs smarter government subsidies to make it happen.
As a side note, you seem to be focused on solar that goes on residential roofs. That’s the worst and most expensive way to do solar. The space available for each project is small, and it’s highly customized to the home’s individual roof situation. It doesn’t take advantage of economies of scale very well. Using the big flat roofs of industrial buildings is better, but the real economies of scale come when you have a large open field. Slap down racks and slap the solar panels on top.
If what you want is energy independence from your local power utility, then I suggest looking into co-op solar/wind farms. If your state bans them–mine does–then that’s something to talk to your state representatives about.
Transmission is tough. But the solution from too much solar investment driving down profits would be to invest that same money into storage. That seems like a natural follow up.
Imagine your profit if you can charge your storage with negative cost power!
It’s one of the solutions, yes.
But let’s look at this more broadly. The idea of combining wind/water/solar/storage with long distance transmission lines isn’t particularly new. The book “No Miracles Needed” by Mark Z. Jacobson (a Stanford Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering) outlined the whole thing in 2023, but was the sum total of the author’s insight that he had had over a decade prior. Dumping all the money in one was never going to get us there.
Capitalism does sorta figure this out, but it takes steps of understanding as it focuses on one thing at a time. The first step dumps money into the thing that’s cheap and gives the best ROI (solar). Then there’s too much of that thing, and the economics shifts to covering up the shortfalls of that part (be it wind or storage or whatever). That makes it better, but there’s still some shortfalls, so then that becomes the thing in demand, and capitalism shifts again.
It does eventually get to the comprehensive solution. The one that advocates in the space were talking about decades before.
The liberal solution–the one that leaves capitalism fundamentally intact–is to create a broad set of government incentives to make sure no one part of the problem gets too much focus. Apparently, we can’t even do that.
Wow, someone actually explaining the problem correctly. I’ll also mention that part of the fix should be on the demand side. Using your home as a thermal battery can load shift HVAC needs by hours, and with a water heater, it works even better. That’s not even talking about all the other things that could be scheduled like washer/dryers, dish washers, EV charging, etc.-
the real economies of scale come when you have a large open field.
And before anyone bothers you about the impact of turning fields into solar farms, I’ll add that we (the US) already have more farmland dedicated to energy production (ethanol corn) than would be necessary to provide our whole electricity demand.
And before anyone bothers you about the impact of turning fields into solar farms, I’ll add that we (the US) already have more farmland dedicated to energy production (ethanol corn) than would be necessary to provide our whole electricity demand.
Oh hell yes. 40% of the corn is grown in the US for ethanol, and it’s a complete and utter waste. Even with extremely optimistic numbers the amount of improvement is close to zero. It might be the worst greenwashing out there; sounds like you’re doing something, but its benefit is likely negative.
We have the land. That’s so not a problem.
It doesn’t take advantage of economies of scale very well.
You missed my point; I was talking about being entirely off-grid there. So unless the homeowner in question also has a large industrial building with a flat roof, we’re back to where I said that they didn’t have enough generative capacity to not be reliant on a power grid, at least in part.
If what you want is energy independence from your local power utility,
No, I want energy independence period. Not just from the local utility, I want independence from a co-op as well. I want to have my own well so I’m not relying on someone else to deliver water. I want enough arable land to grow most, or all, of my own food. This isn’t compatible with living in a city. (And part of the reason I want to generate my own power is so that I can use all electric vehicles.)
You missed my point. What you assumed the article said was completely off base.
No, I want energy independence period. Not just from the local utility, I want independence from a co-op as well.
Then what you’re asking for is a more fractured human society. This kind of independence from others is an illusion and is not compatible with how humans have evolved.
Then what you’re asking for is a more fractured human society.
No, I’m saying I want energy independence. I don’t want to be dependent on the vagaries of service providers, or politicians that decide one day that renewables are great, and then the next day fuck it all drill baby drill, or a utility–or government–that refuses to invest the necessary capital into infrastructure to maintain capability. I’ll pay my taxes so that shit can get done IF that ends up being the will of the people, but I don’t see the point of being dependent on a system that I both need and have no control over.
Drive to get groceries? You’re dependent on most of those same factors.
Water? Same. Even if you have a well, you still don’t want that well to be polluted by people around you.
Shelter? You presumably don’t want a neighbor’s rickety structure to fall over on yours during a storm.
This kind of independence is a farce.
Drive to get groceries? You’re dependent on most of those same factors.
I said I wanted enough arable land to grow my own.
Water? Same. Even if you have a well, you still don’t want that well to be polluted by people around you.
See above.
Shelter? You presumably don’t want a neighbor’s rickety structure to fall over on yours during a storm.
See above. I don’t intend to have neighbors within a mile.
deleted by creator
Negative prices are only mentioned in passing, as a very rare phenomenon
Negative prices are occurring more and more frequently. The cause is baseload generation: it can’t be dialed back as quickly as solar increases during the day, and it can’t be ramped up as fast as solar falls off in the evening. The baseload generators have to stay on line to meet overnight demand. Because they can’t be adjusted fast enough to match the demand curve, they have to stay online during the day as well.
The immediate solution is to back down the baseload generators, and rely more on peaker plants, which can match the curve.
The longer term solution is to remove the incentives that drive overnight consumption. Stop incentivizing “off peak” consumption, and instead push large industrial consumers to daytime operation.
oh no the power is too cheap. God forbid our trillions of tax dollars go to something actually useful and good for the people oh well looks like we will get the F-47 instead and pay it to private military contracts 😂
We need more military! Cut social security!
Why not do something with all that power? In the past there were some projects where they pumped water upstream when there was too much power on the grid. Then on low energy times, the water was released making energy again. Or make hydrogen (I think it was hydrogen). Or do AI stuff
I also seen energie waste machines that basically use a lot of power to do nothing. Only the get rid of all that extra energy so the power grid won’t go down/burn.
Or use it on large scale computing for protein folding simulations, or something.
And yeah, gravity batteries is the best I think we have, with water being the most common medium with pumped-storage hydroelectricity. But the scales of the things are kind of incongruent and… Autoincorrect actually got it right trying to correct that to inconvenient. Still really cool. I think we may need some innovations to cut down on scale issues though. Although it looks like the total power storage available is about one day worth of power for the US in PSH, I’m curious if the instantaneous output is sufficient for the grid and how spread out the storage locations are, as I somewhat doubt they’re often in flatter regions. All in all, I’m not a power engineer, I just know a few and I should bug them sometime.
Why not do something with all that power?
This is a relatively new problem, so it will take awhile for the market to respond to make industries optimized to take advantage of this.
I saw an article a few months ago (couldn’t find it quickly just now) about a small manufacturing company (metals maybe?) that set up shop specifically to run during the excess power events. So its starting to happen, but its not going to be a perfect fit. It means spending lots up front for infra, but only being able to use it a few hours a day cost effectively.
In the past there were some projects where they pumped water upstream when there was too much power on the grid. Then on low energy times, the water was released making energy again.
This is already done with pump hydro. But this needs existing hydroelectric infrastructure to take advantage of. Even then there are usually holding ponds upstream and they themselves have limited capacity.
Or make hydrogen (I think it was hydrogen).
This is being done too at small scales right now. There’s difficulties with it. Hydrogen really sucks to try store and transport. The H2 molecule is so small it leaks out through valves and gaskets that are fine for containing nearly all other gases and liquids. So this means the gear needed is hugely more expensive up front. What a few are doing is using the hydrogen to quickly make Ammonia (NH3), which is much easier to store and contain. However, the efforts doing this are still fairly small.
Or do AI stuff
AI aside, this is one place I haven’t seen develop yet. That being: cheaper compute costs during excess power events.
I suspect its the same problem for the manufacturing. It means spending money on expensive compute infrastructure but only able to use it during the excess power events. As in, the compute in place is already running flat out at full capacity all the time. There’s no spare hardware to use the excess power. If you had spare hardware, you’d add it to your fleet and run it 24/7 making more money.
We still have hydroelectric turbines that can reverse themselves to pump water to a higher elevation reservoir to store surplus energy. We call them pump-gens at my job. The problem is that, as nearby areas develop, that water gets reserved for other things, so they can’t pump it back up because it’s needed further downstream for irrigation or communities or whatever.
Some hobbyists turn up the set point on their electric water heater to store the power as domestic hot water.
Now that’s a good idea! I have a couple of ideas to automate that. Crank the hot water balls out during peak production hours, but cut it off at night. Something like that?
Sounds like a deal for power companies that change prices during on/off peak hours. But wait, am I backwards? Typically peak power costs more? Anyone?
You seem confused.
Peak Solar hours and peak utility rate hours are different. Often both are shorted to “peak hours”.
deleted by creator
Why not do something with all that power?
Because profits are a result of deprivation not progress.
Agree, but there is also profit to be made when using the leftover free power.
deleted by creator
Isn’t it easier just to cover solar panels with reflective material, so they stop producing energy?
deleted by creator
Problems for Capitalism are Solutions for Humanity
See also: Solutions for capitalism are problems for humanity
Wasn’t there a town in China that produced such a glut of surplus electricity that they didn’t know what to do with it? And it was 100% solar?
I guess the biggest bottleneck for renewables is energy storage.
Pretty much. Once we got that covered there is no excuse anymore.
It’s basically solved. Sodium batteries are cheaper and much more durable than lithium batteries, and are currently being commercialized. Their only downside is that they are heavier, but that does not matter for grid-scale storage.
I remember reading about those. Sodium batteries are revolutionary. They don’t need a rare earth mineral… sodium is friggen everywhere.
Being cheaper than Lithium is great, but are they cheaper than nuclear?
The manpower of maintaining all these batteries seems like it would also be a lot, how would you do it for an entire grid, or would you need to have each individual placing a battery on their property to deal with brownouts?
Problem with coal or nuklear is it isn’t cheap. In Germany it survies only on subsidies. And Nuclear was abolished in Germany, a bit to early. I said we needed it 10 years longer and we could have shutdown our coal.
The problem I see with wind and solar is you need backup power, to handle the sinusoidal nature of production. So you need to duplicate your power production, and that costs a lot.
That’s kind of irrelevant.
Nuclear handles the base power generation. Grid storage is meant to handle peaks. It needs to be cheaper than coal, which is also used for peaks.
Anyway, grid storage is already about 200$ per installed kw with lithium. If sodium gets us to 100$, a 1GW installation comparable to a nuclear plant would cost 100 million. That’s like 150 to 300x cheaper than a nuclear plant. And a plant takes years to build, decades even. A storage facility takes days or weeks.
Of course that does not count energy generation, but grid scale storage basically stores free excess energy from nuclear and renewables. So they actually improve the cost efficiency of nuclear and renewables, they don’t compete with them.
That’s the common thought, but it rests on the assumption that demand cannot be manipulated.
Legacy generation incentivized overnight consumption, when the grid had excess production capacity it needed to unload. With solar, we need to reverse those incentives. If it is harder to produce power overnight, we can drive large industry (like steel mills and aluminum smelters) to switch from overnight operations to daytime consumption.
Overnight storage is something we do need, but it is not efficient, and the need for it should be avoided wherever possible.
Parking garages are usually full during the day, when solar is at its highest generation. In the near future, as EV adoption rises, parking garages need charging stations at every space, sucking up every “excess” watt on the grid.
Story of 2010s Germany as well.
I get the sentiment but… When sun isn’t shining the negative prices cause problem for baseline power producers who need to turn off their power plants to avoid the zero to negative power prices.
This causes the power prices to become volatile, since the investments for the power plants that run during the night need to be covered during the night only.
Eventually though the higher price volatility will encourage investments into either demand side adjustability or energy storage systems. This will play out in energy only markets.
The other alternative is to implement a capacity market, which will divide the cost of the baseline production across different production hours by paying producers more for guaranteed production capacity.
Ya I’m not an engineer at all so I’m not sure how hard it is to store that much power but that always seemed like a good idea. Even for electric cars, if we designed a universal battery pack good for a few hundred kilometres that we could swap out at recharge stations I feel like that would be a smart way to do things. But again I have no idea if thats feasible or how it would be implemented.
The problem with batteries is that they are costly to produce if we’re talking about ones that reverse chemical reactions. This is why I rolled my eyes at Elon suggesting we connect batteries to all our renewables. (The cost I learned from Factorio). Other types of batteries, like potential energy buffers are more practical, but also extremely location specific. There is a Technology Connections video about it. Also for example, some rollercoasters have flywheels to slowly build up rotational inertia and then release it all at once. So if we were to store the excess energy, it would probably be done so this way, but baseline power obviously just seems more practical
It’s a problem today, but in 50 years we’re projected to run out of non renewable sources. AI and EVs have the potential to skyrocket energy consumption well beyond our current capacity.
We didn’t really have good batteries at that scale. I believe the large scale power storage is still done using water and gravity. Which is honestly pretty neat, but requires lots of land and a high location.
Much harder than you’d think, though there are some interesting schemes (like huge tanks filled with molten stuff, superconducting rings, giant flywheels). And there’s always a loss with storage.
TBH having a diverse array of power sources (including a little storage) is much better.
Also, batteries in electric cars are unfortunately extremely expensive, and extremely heavy. They’re less efficient than you’d think. Standardization and swappability (and reusing idle batteries for the grid) is a great idea, but even just focusing on the technical aspects, challenging.
interesting! ya this is a whole world I know very little about but it seems very relevant these days.
TBH the best solutions are boring and supply-side. Or regional.
Random examples: heat pumps instead of heaters! Insulation! Geothermal loops or spacer panels for big buildings! Lightweight cars! All would save a hilarious amount of energy, but are way too dull to trend, heh.
…And probably suppressed by industry interest groups. whistles
“Well you see there is generations and generations of ghouls that have made their entire livelihood off the established and continued monopolization of vital resources such as water and power and for some reason the rest of us haven’t gotten together and solved that clear and obvious threat to everyone and everything collectively, I know I don’t get it either.”
They’ve got economist-brain and view everything as a money thing, which is fucked up and a problem.
But negative net demand (the thing “negative cost” is signaling) is a pain in the ass, because you either need to shut off the panels from the grid, find some very high-capacity and high-throughput storage, or blow out your power grid.
Like some hydroelectric dams in Germany get run backwards, pumping water back up behind the wall. I think there are pilot projects to pump air into old mines to build up a pressure buffer. Grid-scale batteries just aren’t there yet.
Solar is good for things where the power demand is cumulative and relatively insensitive to variation over time (like, say, salt pond evaporation, but you don’t actually need panels for that). It’s also good for insolation-sensitive demand (like air conditioning).
Turns out distributed rooftop solar makes more sense given our current grid than big solar farms out in the desert (California built one, it was not a good use of money).
It’s not great, but we need to bite the bullet and use fission+reprocessing in a big way for the near future.
Agreed. It’s framed incorrectly, but the real problem is the “duck curve,” the time disparity between peak generation and peak consumption. Pumped hydro, battery storage, electrolysis, and mechanical storage are all options, but each has its own constraints. Ultimately, though, it’s an engineering problem with viable solutions. We just need the political will for the investment.
Distributed rooftop solar is the worst way to use our grid. It’s designed to pump a lot of power from a single place to a lot of little places. The opposite doesn’t work very well.
The solution is to not focus on solar by itself. Solar/wind/water/storage/long distance transmission need to be balanced with each other. Each has strengths and weaknesses that cover for the strengths and weaknesses of the others.
Distributed rooftop isn’t supposed to be about feeding the larger grid so much as topping off local demand right when it’s needed.
I’m kind of eccentric so I got a humongous array; even then at peak production I was running the A/C for 3-4 houses in my cul-de-sac other than my own. Most installations around where I live are like 1/4 of the size I put up and rarely feed much back.
And home-scale batteries are getting cheap enough that excess won’t necessarily need to get fed into the grid anyway.






















