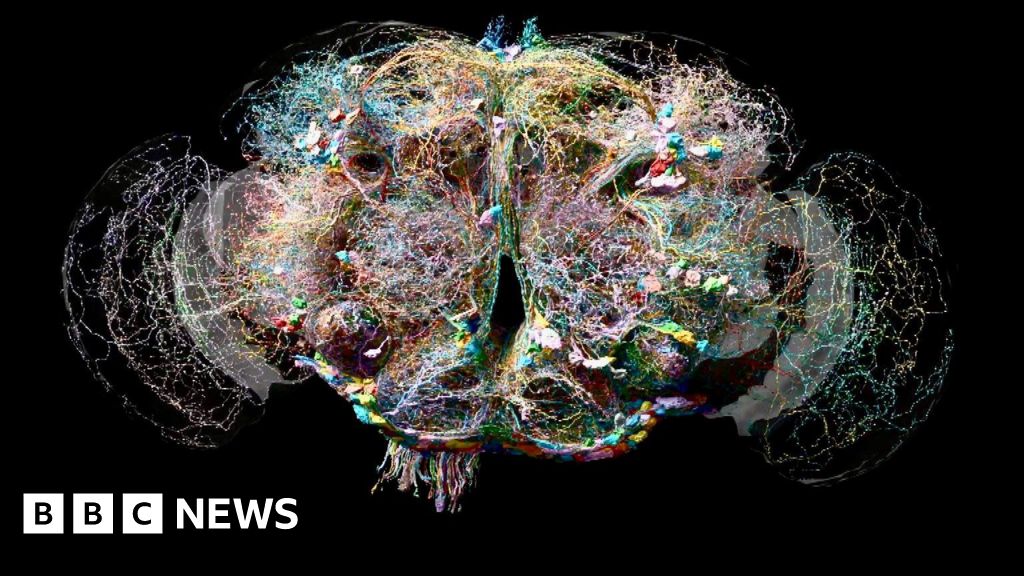
Now for the first time scientists researching the brain of a fly have identified the position, shape and connections of every single one of its 130,000 cells and 50 million connections.
It’s the most detailed analysis of the brain of an adult animal ever produced.
One leading brain specialist independent of the new research described the breakthrough as a “huge leap” in our understanding of our own brains.


Simulate it how? you need an initial state.
Also connections to nerve cells are not constant. Some connections are strong and the nerve cell is more likely to activate when triggered through one of them while other are weak and need stronger signal to trigger (someone who knows biology can rephrase this part better). so with 50 million connections of varying strength simulation becomes much more difficult.
The other thing is that 99% of the time the brain respond to outside stimuli. You see something, signal is sent to brain and brain make decision based on the input.
In this case you have absolutely zero input.
I don’t see why adding weights to the connections would be particularly difficult. Even if the weights need to vary over time or by other conditions, that could be included in the simulation. It might be a bit more complex, but current neural network systems already do variable connection strength between nodes.
This should be very easy - if we’re simulating the presence of sensory neurons then we can certainly simulate some input stimuli on them.
I don’t see why this would be true, and anyway how do you know that the connection map doesn’t already represent an initial state?